Immuno Delivery (Focus Group - ID)
(236) pH-Sensitive Zinc-Zoledronate Inhalation Therapy for Macrophage Modulation in Lung Cancer
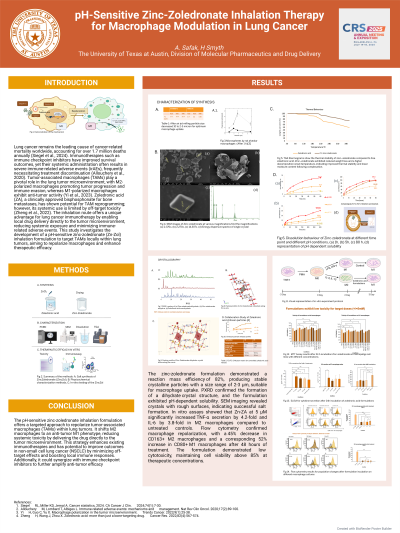
Introduction: Lung cancer causes over 1.7 million deaths yearly (1). While immune checkpoint inhibitors improve survival, they often cause irAEs, leading to treatment discontinuation (2). Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) are key in lung tumors, with M2 promoting growth and M1 showing anti-tumor effects (3). Zoledronic acid (ZA) can reprogram TAMs but is limited by off-target toxicity (4). Inhalation delivers drugs directly to tumors, reducing systemic exposure and irAEs. This study develops a pH-sensitive zinc-zoledronate (Zn-ZA) inhalation to repolarize TAMs and improve efficacy.
Learning Objectives:
- Participants will be able to explain tumor-associated macrophage (TAM) modulation mechanisms.
- Participants will be able to show how pH-sensitive inhalation enhances lung cancer immunotherapy.
- Participants can outline the benefits and challenges of localized drug delivery in cancer.
Hugh Smyth, Ph.D., University of Otago – Professor, Molecular Pharmaceutics and Drug Delivery, The University of Texas at Austin
.jpg)
Arifenur Safak
PhD Candidate
The University of Texas at Austin
Austin, Texas, United States

