Nanomedicine and Nanoscale Delivery (Focus Group - NND)
(510) Comparative ex vivo permeability through healthy and inflamed skin hydrophilic and hydrophobic >500 Da drugs using lipid-based nanovesicles
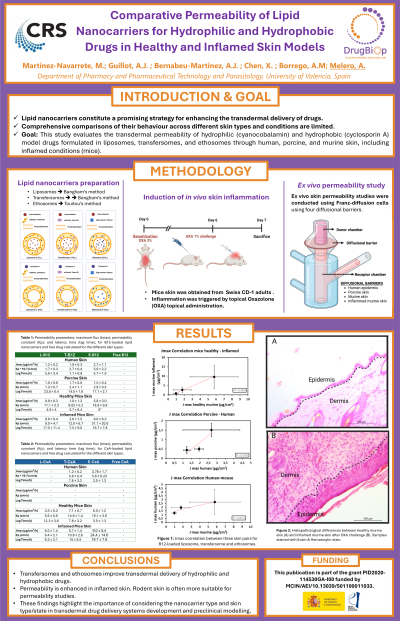
Co-Authors: Miquel Martínez-Navarrete 1 , Alejandro Bernaveu-Martinez 1 , Ana Borrego-Sanchez 1 , Xuefan Chen 1 , Antonio Jose Guillot 1 , Ana Melero 1 Department of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Technology and Parasitology. University of Valencia. Avenida Vicente Andres Estelles SN, 46100, Burjassot, Valencia, Spain.
Introduction:
Lipid-based nanovesicles constitute a promising strategy for enhancing the transdermal delivery of drugs, particularly those ones with poor skin permeability and molecular weight >500 Da. However, comprehensive comparisons of their behavior across pathological tissues are limited. This study evaluates the transdermal permeability of hydrophilic (cyanocobalamin) and hydrophobic (cyclosporin A) drugs formulated in different types of lipid-based nanovesicles (liposomes, transfersomes, and ethosomes) through murine (healthy and inflamed), human and porcine skin.
Introduction:
Lipid-based nanovesicles constitute a promising strategy for enhancing the transdermal delivery of drugs, particularly those ones with poor skin permeability and molecular weight >500 Da. However, comprehensive comparisons of their behavior across pathological tissues are limited. This study evaluates the transdermal permeability of hydrophilic (cyanocobalamin) and hydrophobic (cyclosporin A) drugs formulated in different types of lipid-based nanovesicles (liposomes, transfersomes, and ethosomes) through murine (healthy and inflamed), human and porcine skin.

Ana Melero, PhD (she/her/hers)
Associate Professor
University of Valencia, Spain

